Grapes or Raisins?
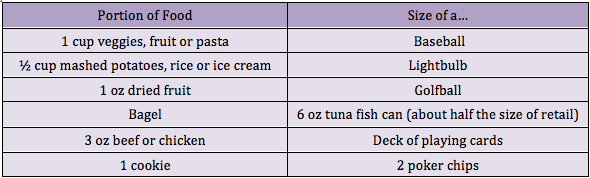
Almost everyone who is health conscious agrees that American food portions are out of control! One of our most visited blogs "Eat less, Move More" has generated a lot of comments and many readers are surprised how small portions need to be if you want to lose weight. We've also received a number of suggestions like using a smaller plate, eating 5-6 mini meals every day, etc. But the bottom line remains the same: If you want to actually lose weight and you are not an exercise buff, portion control is a good way to go. However, not all portions represent the same amount of calories.
Feel fuller on fewer calories. This requires understanding the concept of "energy density". Energy density is the number of calories (energy) in a certain amount of food. High energy density means that there are a lot of calories in a small amount of food. Low energy density means there are few calories in a lot of food.
One of the classic examples is raisins vs. grapes. A one cup of raisins (dried grapes) has about 434 calories. A cup of fresh grapes has about 104 calories. So to eat the same amount of calories, you would have to limit the raisins to 1/4 a cup! Which choice would make you feel fuller? One ounce of potato chips is 150 calories, the same amount of calories found in 3 1/2 cups of air popped popcorn.
In order to lose or maintain your weight, your goal should be to eat more low energy dense foods. That way, you eat larger portions that make you feel fuller. Let's explore this density concept a bit further. Several factors play a role in what makes food high or low in energy density.
1. Water. Fruits and vegetables have a high water content which provides volume but not calories, making them a low energy dense food. A grapefruit is 90 percent water and a half grapefruit is only 39 calories. Watermelon is 92% water.
2. Fiber. High fiber foods provide volume and take longer to digest, making you feel fuller with less calories.
3. Fat. Fat is very high in energy density (remember we are really talking about calories!). One teaspoon of butter contains almost the same number of calories as 2 cups of low energy dense broccoli.
What about nutrition? Does "fullness" translate into a adequate nutritional intake? What foods are better options when it comes to energy density?. According to the Mayo Clinic Health Weight Pyramid:.
- Most vegetables are low in calories but high in volume especially lettuce, asparagus, broccoli and zucchini. Add more vegetables to your pastas instead of meat and cheesy sauces. Put veggies on your sandwiches instead cheese slices and gobs of mayonnaise.
- Fruits are healthy but some are lower calorie choices than others and certain fruits have more concentrated sugars (such as raisins) and have higher calories with less volume. Fruit juices are also relatively high in calories and don't necessarily fill you up. Eating a whole orange with its natural fiber will fill you up more than a glass of orange juice.
- Carbohydrates are either grains or foods made from grains like cereals and pasta. Select carbs that are higher in fiber like oatmeal, whole grain breads, brown rice and avoid breads made with refined white flour and sweeteners.
- Fats are a high energy dense food but some are healthier than others. Watch your portions and include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats in your diet like nuts, seeds, healthier vegetable oils (flax see, olive, and safflower oil). Just keep the portions small.
- Sweets are high in energy density and are a challenge when it comes to caloric intake. Try to find desserts that have low fat and sugar content, such as fruits and low-fat yogurt. If they are baked, look for whole grain flour pastries. The key to limiting the effect of sweets is to keep the servings small (share with your table mates--1 dessert, 4 forks--most restaurants are accommodating).
- Protein comes from plant and animal sources and the healthiest low-energy dense choices are those high in protein but low in fat such as lentils (also high in fiber!), skinless white meat, and fish. Select fat-free dairy foods.
Substituting low density foods keep you from feeling food deprived, make you feel better about your meal and will help keep those calories down! Here's a final example: A small order of McD's french fries has 225 calories. You could substitute (with the same amount of calories) a salad made with a small apple, 10 cups of fresh spinach, and 1 1/2 cups strawberries with a splash of diet dressing.
 The news of the government shutdown has by now reached everyone’s ears and has sparked questions and concerns about the state of our nation. While several groups are directly affected in this stalemate, special attention must be drawn to the 9 million low-income women and children who may be adversely affected around the country. These women and children rely on the government for food assistance through the “Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children,” known colloquially as the Women and Infant Children Program (WIC). Douglas Greenaway, president and CEO of the National WIC Association, said that the state programs that serve this population may run out of money as early as next week, while others may be able to stay afloat until the end of the month. The WIC clinics are funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, so when Congress fails to approve funding, it leaves WIC clinics, and the women and children they serve, in the lurch. Since WIC programs are run by states through grants from the federal government, it is unclear which states will be hit harder than others.
The news of the government shutdown has by now reached everyone’s ears and has sparked questions and concerns about the state of our nation. While several groups are directly affected in this stalemate, special attention must be drawn to the 9 million low-income women and children who may be adversely affected around the country. These women and children rely on the government for food assistance through the “Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children,” known colloquially as the Women and Infant Children Program (WIC). Douglas Greenaway, president and CEO of the National WIC Association, said that the state programs that serve this population may run out of money as early as next week, while others may be able to stay afloat until the end of the month. The WIC clinics are funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, so when Congress fails to approve funding, it leaves WIC clinics, and the women and children they serve, in the lurch. Since WIC programs are run by states through grants from the federal government, it is unclear which states will be hit harder than others.