 Older, postmenopausal women who take popular medications to control indigestion and heartburn called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may put themselves at higher risk for hip fractures according to new research by Dr. Hamed Khalili, from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. Long-term use of these drugs may increase that risk by 35 percent and even higher (to 50 percent) in smokers. Some examples of these medications are shown here.
Older, postmenopausal women who take popular medications to control indigestion and heartburn called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may put themselves at higher risk for hip fractures according to new research by Dr. Hamed Khalili, from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. Long-term use of these drugs may increase that risk by 35 percent and even higher (to 50 percent) in smokers. Some examples of these medications are shown here.
According to the researchers, PPIs are strongly indicated in some patients for short term use, but they should be closely monitored if long term use is needed. Dr. Khalili's data supports the recent decision by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to revise labeling of PPIs to incorporate concerns about a bone fractures with use of these products.
For the study, they looked at data from 80,000 postmenopausal women. .Over the course of eight years, almost 900 hip fractures occurred -- a 35 percent increased risk for women using PPIs compared to women who didn't take the drugs. In absolute terms, the risk of hip fracture works out to about 2.02 fractures for every 1,000 person years for those taking PPIs, compared with 1.51 fractures per 1,000 person years. Person years are the number of years in a study multiplied by the number of people in the study. The increased risk of fractures among women who smoked was even higher. The longer a women took a PPI, the more her risk increased.
In 2000, 6.7 percent of the women used PPIs regularly, generally for acid reflux; by 2008 that had jumped to 18.9 percent. This could mean that more fractures will be seen in years to come. Women who stopped using PPIs saw their risk of hip fracture return to normal within two years, Khalili's group noted. Women are also cautioned not to suddenly quit their PPI and gradual tapering is recommended to avoid acid rebound. Often, calcium supplements are used to bolster bone strength, but because PPIs affect the absorption of calcium, taking calcium supplements may not be effective. The researchers did take calcium supplement use into account and the risk remained.
SOURCE: Jan. 31, 2012, BMJ, online

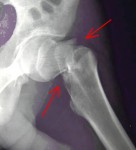 Painful Hip Fractures Strike Breast Cancer Survivors
Painful Hip Fractures Strike Breast Cancer Survivors