 Seven out of 10 women in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Central Asia and Southeast Asia who want to avoid pregnancy but are not using modern contraceptives report reasons for nonuse that indicate currently available methods do not satisfy their needs, according to new Guttmacher research. The findings suggest that substantially bringing down unintended pregnancy rates in these developing regions will require increased investment in the development of new methods that better address women’s concerns and life circumstances.
Seven out of 10 women in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Central Asia and Southeast Asia who want to avoid pregnancy but are not using modern contraceptives report reasons for nonuse that indicate currently available methods do not satisfy their needs, according to new Guttmacher research. The findings suggest that substantially bringing down unintended pregnancy rates in these developing regions will require increased investment in the development of new methods that better address women’s concerns and life circumstances.
The report, Contraceptive Technologies: Responding to Women’s Needs, focuses on the three regions that together account for the majority of women in the developing world with an unmet need for contraception. Overall, 40% of pregnancies in these regions—about 49 million—are unintended. Each year, these pregnancies result in 21 million unplanned births, an equal number of abortions (three-quarters of which are unsafe) and 116,000 maternal deaths.
“The findings make clear that meeting the need for contraception requires not only increased access and counseling, but the development of new methods that better meet women’s needs,” says Jacqueline E Darroch, senior fellow at the Guttmacher Institute and one of the study’s authors.
To gain insight into why so many women in developing countries are not using modern contraceptives, researchers analyzed nationally representative data from Demographic and Health Surveys and other sources. They found that the majority of women with an unmet need for contraception are 25 or older and live in rural areas, and about four in 10 are poor. The reasons women most frequently given for not using a method are concerns about health risks or side effects (23%); infrequent sex (21%); being postpartum or breast-feeding (17%); and opposition from their partners (10%).
The findings shed light on the types of methods that could have the greatest impact on increasing contraceptive use: Developing new contraceptive methods that have negligible side effects, are appropriate for breast-feeding women and could be used on demand has the potential to greatly reduce unmet need for contraception. So would methods that women can use without their partner’s knowledge.
The report shows that overcoming method-related reasons for contraceptive nonuse could reduce unintended pregnancy by as much as 59% in these regions. Unintended births and induced abortions could be reduced by similar proportions, and 70,000 maternal deaths could be prevented. However, the researchers note that new contraceptive methods alone will not overcome all reasons for nonuse. Other causes, including poor access to and quality of contraceptive services must also be addressed.
Currently, 104 million women in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Central Asia and Southeast Asia have an unmet need for modern contraceptive methods because of method-related reasons. Taking into account projected population growth, this number will increase to 161 million in the next four decades if concerns about currently available methods are not addressed. The researchers note that there has been a lack of attention and resources dedicated to contraceptive research and development, and that there is a vital, immediate need to reinvigorate the field.
In addition to long-term work to develop new contraceptive methods, they point out that adaptations to current methods could make them more widely acceptable and easier to use. They conclude that immediate headway toward satisfying unmet need could be made by ensuring that women and couples receive more accurate information about the risk of unintended pregnancy and have greater access to quality counseling and services that offer a range of methods.
The report, Contraceptive Technologies: Responding to Women’s Needs, was funded by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The findings and conclusions contained within are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect positions or policies of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
back to top
Source: Guttmacher Institute

 Staying up late every night and sleeping in is a habit that could put you at risk for gaining weight. People who go to bed late and sleep late eat more calories in the evening, more fast food, fewer fruits and vegetables and weigh more than people who go to sleep earlier and wake up earlier, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Staying up late every night and sleeping in is a habit that could put you at risk for gaining weight. People who go to bed late and sleep late eat more calories in the evening, more fast food, fewer fruits and vegetables and weigh more than people who go to sleep earlier and wake up earlier, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study. National Association of Colleges and Employers. The report found that females with new bachelor degrees were offered an average of $36,451 compared to $44,159 for their male counterparts. Even when salary is adjusted by college major (14 were included), men come out ahead in all except two areas: engineering and liberal arts/humanities. Report author Edwin Koc noted that while gender pay disparities are often linked to women more frequently leaving the work force, he did not feel that was the cause in this study.
National Association of Colleges and Employers. The report found that females with new bachelor degrees were offered an average of $36,451 compared to $44,159 for their male counterparts. Even when salary is adjusted by college major (14 were included), men come out ahead in all except two areas: engineering and liberal arts/humanities. Report author Edwin Koc noted that while gender pay disparities are often linked to women more frequently leaving the work force, he did not feel that was the cause in this study.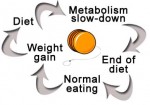 Have you been losing weight and despite staying on your diet and exercising, your weight suddenly stays the same? Don't get discouraged, it's normal for weight loss to slow down and even stop. This phenomenon is called the "weight-loss plateau" and it's more common than you think. Even the best planned weight loss program can become stalled.
Have you been losing weight and despite staying on your diet and exercising, your weight suddenly stays the same? Don't get discouraged, it's normal for weight loss to slow down and even stop. This phenomenon is called the "weight-loss plateau" and it's more common than you think. Even the best planned weight loss program can become stalled. Green tea has become an international mainstay beyond the Orient. Many observational studies have shown that green tea is full of potent polyphenols (an antioxidant) that lower the risk of several chronic degenerative diseases such as heart disease and osteoporosis. A recent study from Dr. Chwan-Li (Leslie) Shen, an associate professor and a researcher at the Laura W. Bush Institute for Women's Health at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center looked at the mechanism behind this correlation and believes it may have to do with lowering chronic levels of inflammation.
Green tea has become an international mainstay beyond the Orient. Many observational studies have shown that green tea is full of potent polyphenols (an antioxidant) that lower the risk of several chronic degenerative diseases such as heart disease and osteoporosis. A recent study from Dr. Chwan-Li (Leslie) Shen, an associate professor and a researcher at the Laura W. Bush Institute for Women's Health at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center looked at the mechanism behind this correlation and believes it may have to do with lowering chronic levels of inflammation. groups:
groups: A new
A new  According to a new
According to a new 
 Certain hairstyles such as braids and weaves may increase the risk of a irreversible type of baldness called Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA) that starts at the central part of the scalp and spreads out toward the edge of the hairline.
Certain hairstyles such as braids and weaves may increase the risk of a irreversible type of baldness called Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA) that starts at the central part of the scalp and spreads out toward the edge of the hairline. According to a study published in the
According to a study published in the  Federal regulators say some companies are selling products that make unproven claims to treat sexually transmitted diseases—claims that could pose a threat to public health. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says only prescription medicines and diagnostic tools available through a health care professional are effective for STD diagnosis and treatment. FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) are warning manufacturers and distributors that they could face legal action if the products aren’t removed from the market. The agencies say at least 15 products claim to treat, prevent, or cure STDs and are being sold online and at some retail outlets.
Federal regulators say some companies are selling products that make unproven claims to treat sexually transmitted diseases—claims that could pose a threat to public health. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says only prescription medicines and diagnostic tools available through a health care professional are effective for STD diagnosis and treatment. FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) are warning manufacturers and distributors that they could face legal action if the products aren’t removed from the market. The agencies say at least 15 products claim to treat, prevent, or cure STDs and are being sold online and at some retail outlets.